The Urgent Need for Smart Urban Planning Design Today
The need for intelligent urban planning design has never been more urgent.
When designing urban infrastructures, there is much to consider, from creating walkable neighbourhoods to integrating green spaces and public transportation. Architects and city planners must also overcome significant challenges.
We explore the importance of efficient urban planning design and delve into the critical challenges faced in creating sustainable and livable cities.
What is Urban Planning Design and Why Does it Matter?
In the rapidly changing landscape of modern cities, urban planning design is a vital discipline that shapes the very fabric of society. It involves envisioning and crafting functional and physical forms that bring cities to life, harmonising the diverse needs of residents, infrastructure, economic development, and ecological systems.
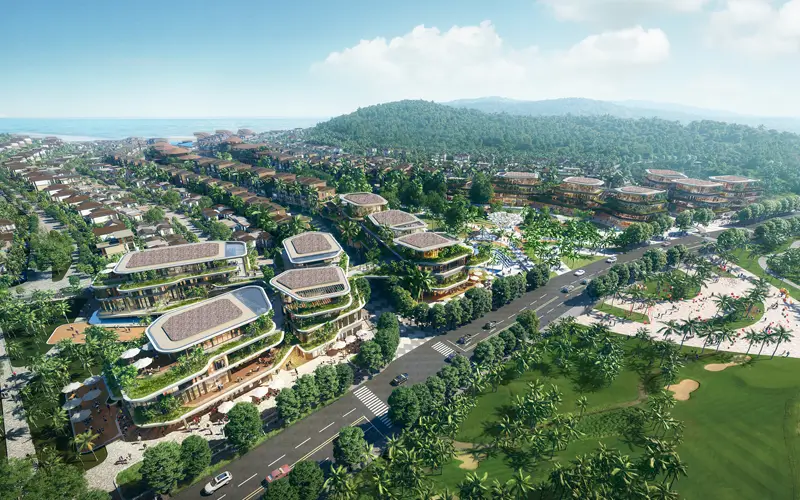
Designing a catalyst of beachfront living combining live, shop, eat, and play for Starfish Beach Resort
Urban design follows principles that prioritise sustainability, liveability, and efficiency. These principles entail integrating residential, commercial, and public spaces to ensure a seamless flow of activities and services. They also address transportation planning, green spaces, and public infrastructure to enhance the quality of life for residents.
Well-designed cities improve the daily experiences of their citizens and contribute to economic growth, environmental preservation, and social cohesion.
Furthermore, urban planning design plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges posed by climate change and environmental degradation. Thoughtful urban planning is essential in today’s rapidly changing world, driven by factors such as population growth, urbanisation, climate change, sustainability, economic development, competitiveness, social equity, and inclusion. This involves tackling issues such as affordable housing, the impacts of climate change, economic competitiveness, and inclusive urban planning to address social challenges.
By incorporating sustainable urban design principles, cities can reduce their carbon emissions, promote energy efficiency, and preserve natural environments through initiatives such as urban forests and innovative water management systems.
Challenges in Urban Planning Design
Urban planning presents a complex balancing act, aiming to reconcile economic growth with environmental sustainability and social equity to create economically vibrant, sustainable, and livable cities.
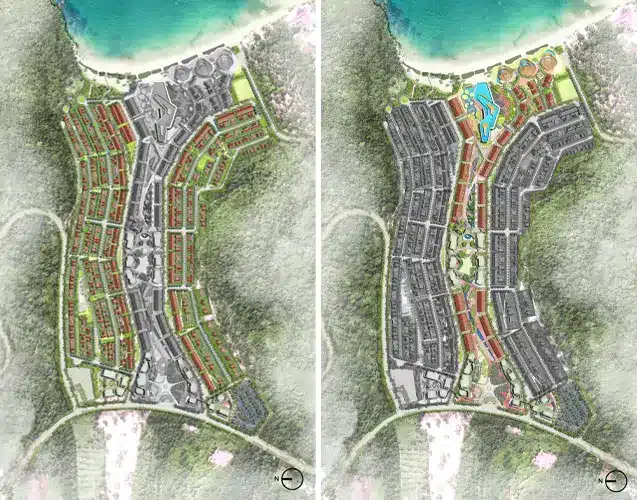
Introducing greeneries around the perimeters and extending to higher levels in Brigade Icon
One of the main challenges involves integrating green spaces within urban areas. These spaces are vital for improving air quality, addressing climate change, and enhancing residents’ well-being. However, as cities expand, the pressure to develop land for housing and businesses often threatens these essential green spaces.
Another significant challenge is developing efficient public transportation systems. These systems are crucial for reducing traffic congestion, improving accessibility, and promoting sustainable mobility. Yet, the required investment and the need to retrofit existing infrastructure can present formidable obstacles.
Urban planners also face the conflicting demands of economic development and environmental protection. As cities grow, the demand for space and resources increases, often at the expense of the environment. The challenge lies in finding a balance that allows for growth while preserving the natural environment.
The Key Elements of Effective Urban Planning Design
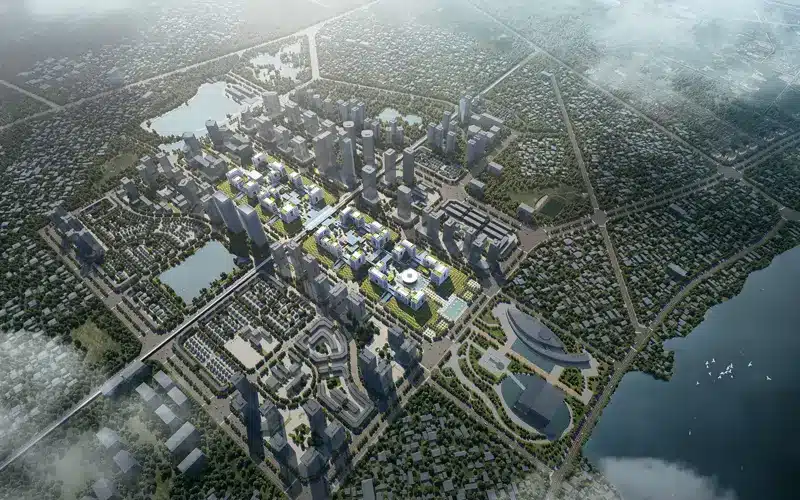
Strategic placement of private and public programs in 12 Ministries with seamless accessibility
Successful urban planning design hinges on several critical elements that work in harmony to create vibrant, livable communities.
Human-Centric Design
Effective urban planning prioritises people by creating pedestrian-friendly spaces, accessible public transportation, and ample green areas for recreation. This approach fosters a sense of community and promotes active lifestyles.
Mixed-Use Development
Integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within close proximity reduces reliance on automobiles and encourages walkability. This mixed-use approach creates dynamic neighbourhoods where people can live, work, and play.
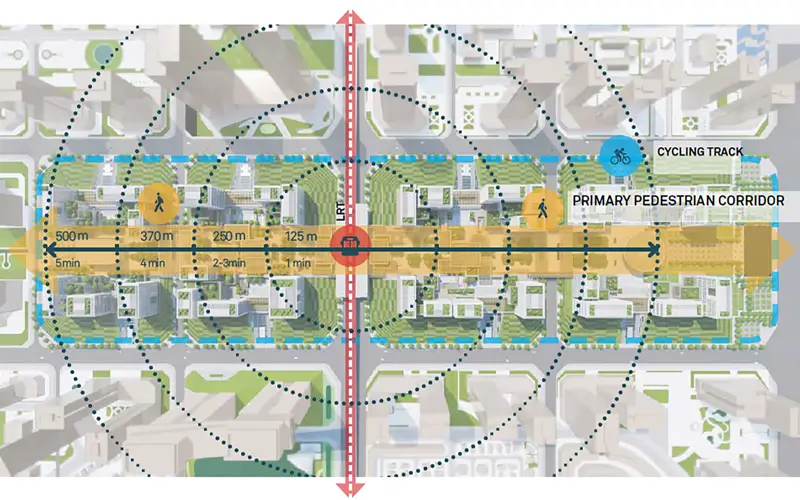
Connectivity and Accessibility
Thoughtful consideration of connectivity and accessibility for 12 Ministries masterplan
Well-designed urban areas feature a network of pedestrian pathways, bike lanes, and efficient public transportation systems. Ensuring easy navigation for all community members, regardless of age or ability, is critical to fostering inclusivity.
Sustainability and Resilience
Incorporating green spaces and eco-friendly practices — such as energy-efficient buildings and waste management systems—supports sustainable urban growth. Resilient design principles also help cities adapt to challenges like climate change and natural disasters.
Preservation of Cultural Identity
Celebrating a city’s unique cultural heritage is achieved through the conservation of historic buildings, public art, and the thoughtful integration of local architectural styles and materials. This ensures that new developments respect and enhance the city’s character.
By focusing on these key elements, urban planners and designers can create cities that are not only visually appealing but also functional, sustainable, and responsive to the evolving needs of the people.
The Role of Technology in Modern Urban Planning Design
Using axonometries to provide a clear and accurate representation of Argon’s form and spatial relationships
Innovative technologies have revolutionised urban planning, changing the way cities are designed, built, and managed. Advanced software and digital urban design tools have empowered architects to create more sustainable and efficient cities.
One of technology’s most profound impacts lies in its capacity to gather and analyse real-time data. Big data and sophisticated analytics have empowered us to acquire insights into various facets of urban life, such as traffic patterns, energy consumption, and population dynamics. The data-driven approach enables more astute decision-making, leading to efficient urban design solutions that cater to each city’s distinct challenges and needs.
Additionally, advanced modelling and simulation tools enable the creation of detailed 3D models, simulate different scenarios, and visualise the impact of designs on the surrounding environment. This enhances collaboration among stakeholders and facilitates effective communication.
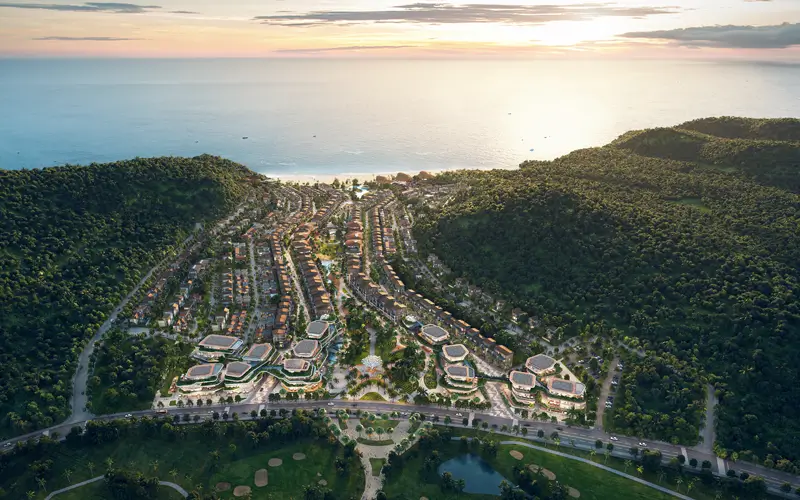
Using technology to provide top-down perspectives of the layout, relationships and different elements within the Starfish Beach Resort masterplan
Smart cities, a concept that integrates technology into every aspect of urban development, are rapidly gaining traction. By leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and other innovative technologies, we can create intelligent infrastructure that adapts to changing conditions and optimises resource utilisation.
Embrace the Future of Urban Living with Smart Urban Planning Design
Urban planning design is essential for creating functional, vibrant, resilient, and adaptable cities that cater to the changing needs of their inhabitants. It goes beyond aesthetics, considering social, economic, and environmental factors that shape urban life.
As technology evolves, its role in shaping sustainable cities becomes increasingly significant. Striking the right equilibrium is crucial for sustainable development. Innovative approaches in urban design, like mixed-use zoning and transit-oriented development, help cities meet the complex demands of the modern metropolis. Urban planners continue to play a critical role in creating vibrant, liveable cities that foster economic prosperity and environmental stewardship through foresight and balanced priorities.